Diabetes
Patients with different types of diabetes mellitus frequently show alterations in pancreatic morphology and exocrine function. PEI can therefore occur as a result of long-standing type 1 and type 2 diabetes.1,2
- In a 2015 audit, 24% of patients with diabetes had abnormal stools (score 5 on the Bristol Stool Chart), steatorrhoea or unexplained weight loss3
- 42% of symptomatic patients who provided a stool sample had FE-1 levels indicative of PEI3
One study examined the efficacy of Creon® in patients with tropical calculous pancreatitis, a form of chronic pancreatitis largely attributed to malnutrition that’s prevalent in India and other Afro-Asian countries in which patients present with abdominal pain, pancreatic calculi and insulin-resistant diabetes.4
After 6 months of Creon® treatment patients achieved better control of diabetes, improvement in abdominal symptoms and overall sense of well being.4 This included a significant reduction in post-prandial plasma glucose and glycosylated haemoglobin at six months vs. baseline.4
Significant reduction in post-prandial plasma glucose and glycosylated haemoglobin at baseline vs. 6 months treatment with Creon® (total dose 8,000 lipase units)4
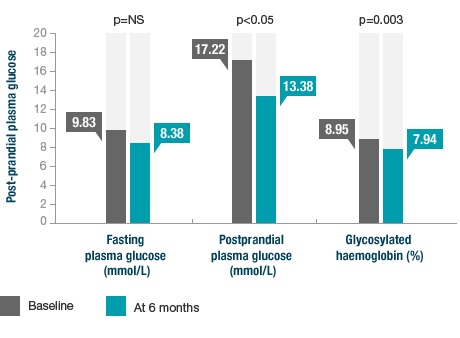
Adapted from Mohan V et al. Int J Pancreatol. 1998.
Furthermore, these patients showed significant improvements in PEI symptoms, including the following:4
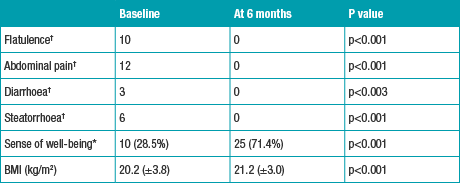
References
- Hardt PD and Ewald N. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in diabetes mellitus: a complication of diabetic neuropathy or a different type of diabetes? Exp Diabetes Res. 2011; 761950. Epub 2011 Aug 1.
- Ewald N and Hardt PD. Diagnosis and treatment of diabetes mellitus in chronic pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19(42): 7276-7281
- Cummings MH, et al. Gastrointestinal symptoms and pancreatic exocrine insufficiency in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Practical Diabetes. 2015; 32(2): 54-58
- Mohan V, et al. Oral pancreatic enzyme therapy in the control of diabetes mellitus in tropical calculous pancreatitis. Int J Pancreatol. 1998; 24(1): 19-22
- Löhr J-M, et al. Synopsis of recent guidelines on pancreatic exocrine insufficiency. United European Gastroenterol J. 2013; 1(2): 79-83
Viatris Connect is an online platform for UK healthcare professionals.
Across the website you will find news, blogs and product information.
Register to Viatris Connect today
Please note that the website contains promotional and non-promotional material including educational content and resources to help you and your patients.
REGISTER NOW
 Read now
Read now

