Cystic fibrosis
Studies have shown that PEI occurs in more than 85% of patients with cystic fibrosis.1 Malnutrition and growth failure are important prognostic factors in children with cystic fibrosis and both may adversely affect the course of the disease with declining lung function and poor outcomes.2 Population-based studies in both adults and children with cystic fibrosis have shown a clear association between normal growth status and both pulmonary function and survival.3
Adult cystic fibrosis and PEI
Following a parallel design of 2 randomised placebo-controlled studies with an open-label run-in-phase whereby all patients were stabilised on Creon®, patients who were then randomised to Creon® experienced positive improvement in the mean coefficient of fat absorption (CFA), unlike those randomised to placebo, whose mean CFA decreased significantly (p<0.001).4
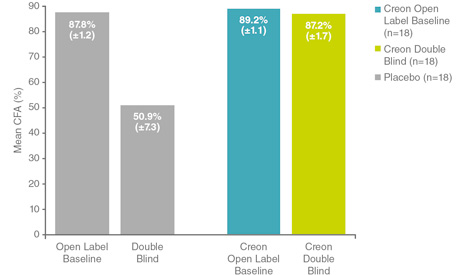
Dose of pancreatin: 4537.8 mean lipase units/kg/day.
Adapted from Stern RC et al. Am J Gastroenterol 2000.
Infant and child cystic fibrosis and PEI
In infants with cystic fibrosis aged 1 to 24 months, Creon® produced a rapid improvement in mean coefficient of fat absorption (CFA).2
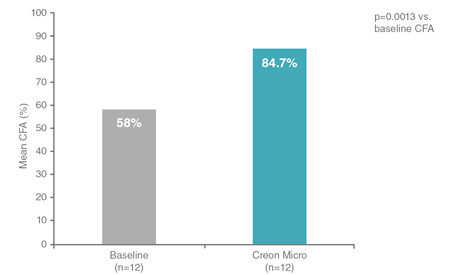
CFA:Coefficient of fat absorption
Adapted from Colombo C et al. Pancreas 2009.
Furthermore, treatment with Creon® Micro was found to:2
- increase length and weight over 8 weeks
- decrease the proportion of patients with steatorrhoea from 100% to 58% at 2 weeks
- increase the number of patients with normal stool characteristics at 2 weeks
- reduce mean faecal energy loss at 2 weeks
References
- Littlewood JM, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of intestinal malabsorption in cystic fibrosis. Pediatric Pulmonology. 2006; 41(1): 35-49
- Colombo C, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of Creon for Children in infants and toddlers with pancreatic exocrine insufficiency caused by cystic fibrosis: an open-label, single-arm, multicenter study. Pancreas. 2009; 38(6): 693-699
- Stallings VA, et al. Evidence-based practice recommendations for nutrition-related management of children and adults with cystic fibrosis and pancreatic insufficiency: results of a systematic review. J Am Diet Assoc. 2008; 108(5): 832-839
- Stern RC, et al. A comparison of the efficacy and tolerance of pancrelipase and placebo in the treatment of steatorrhea in cystic fibrosis patients with clinical exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000; 95(8): 1932-1938
Viatris Connect is an online platform for UK healthcare professionals.
Across the website you will find news, blogs and product information.
Register to Viatris Connect today
Please note that the website contains promotional and non-promotional material including educational content and resources to help you and your patients.
REGISTER NOW
 Read now
Read now

