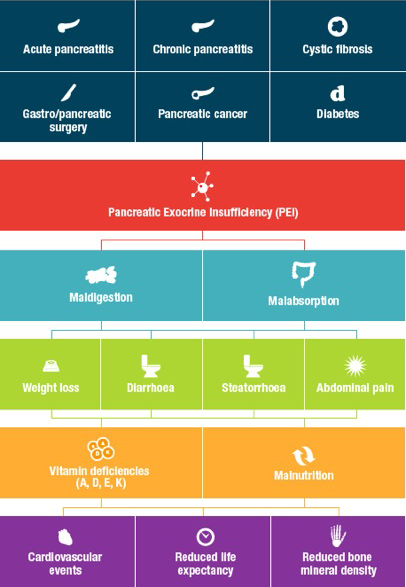
Most common causes of PANCREATIC EXOCRINE INSUFFICIENCY
PEI may be present in patients with:1
- acute pancreatitis
- chronic pancreatitis
- cystic fibrosis
- post gastric and/or pancreatic surgery
- pancreatic cancer
- other conditions such as diabetes mellitus, coeliac disease, Crohn's disease
In fact, any pathology that affects the digestion of food by pancreatic enzymes – including extrapancreatic conditions – may cause PEI.
Irrespective of your patient’s primary condition, the consequences of undiagnosed or untreated PEI are both acute and long-term. Untreated PEI can lead to malnutrition and fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies,2 which are related to high morbidity and mortality secondary to an increased risk of malnutrition-related complications, including:
- reduced quality of life3
- reduced bone mineral density4
- cardiovascular events2,5
Causes and consequences of untreated PEI
GOALS OF PANCREATIC ENZYME REPLACEMENT THERAPY (PERT)
All patients with PEI should receive PERT, regardless of the presence or degree of steatorrhoea and associated symptoms.2,4–7 PERT facilitates the digestion of fats, proteins and carbohydrates by replacing missing digestive enzymes in patients with PEI.2
The treatment goals of PERT for PEI are to:5
- Treat symptoms of PEI and improve nutritional status, including:
- increase fat absorption and reduce steatorrhoea*
- reduce stool frequency
- improve stool consistency
- Mimic the normal physiological conditions of a healthy pancreas, when the correct dosage and timing of administration is used.1
*Steatorrhoea is a late-stage symptom and occurs when over 90% of normal pancreas function is lost. Hence, diagnosis should be made before the presence of steatorrhoea.
References
- Keller J, et al. Human pancreatic exocrine response to nutrients in health and disease. Int J Pancreatol. 2005; 54(Suppl 6): 1-28
- Toouli J, et al. Management of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency: Australasian Pancreatic Club recommendations. Med J Aust. 2010; 193(8): 461-467
- Ockenga J. Importance of nutritional management in diseases with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. HPB (Oxford). 2009; 11(3): 11-15
- Sikkens ECM, et al. Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy in chronic pancreatitis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2010; 24(3): 337-347
- Domínguez-Muñoz JE. Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency: diagnosis and treatment. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 26(Suppl 2): 12-16
- Domínguez-Muñoz JE. Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy for pancreatic exocrine insufficiency: when is it indicated, what is the goal and how to do it? Adv Med Sci. 2011; 56(1): 1-5
- Domínguez-Muñoz JE and Iglesias-García J. Oral pancreatic enzyme substitution therapy in chronic pancreatitis: is clinical response an appropriate marker for evaluation of therapeutic efficacy? Journal of the Pancreas. 2010; 11(2): 158-162
- Gastroenterology and Endoscopy News. Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency. Part 1 of 2: Pathogenic and Diagnostic Considerations. Available at: https://www.gastroendonews.com/download/Pancreatic_CaPart1_WM.pdf. Last accessed: December 2023
Viatris Connect is an online platform for UK healthcare professionals.
Across the website you will find news, blogs and product information.
Register to Viatris Connect today
Please note that the website contains promotional and non-promotional material including educational content and resources to help you and your patients.
REGISTER NOW
 read more
read more

